Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Cs) on the coastal seafloor near the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant inferred from radiocesium distributions in long cores
Cs) on the coastal seafloor near the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant inferred from radiocesium distributions in long coresNakanishi, Takahiro; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Misono, Toshiharu; Shiribiki, Takehiko; Urabe, Yoshimi*; Sanada, Yukihisa
Journal of Coastal Research, 116(SI), p.161 - 165, 2024/01
Continuous data of Cs-137 concentration in surface seabed sediment around the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) from 2012 to 2022 was compiled and its temporal change was fitted by exponential function. In general, Cs-137 concentrations were gradually declining with time. However, at some monitoring points in shallow region, long half-lives and/or large deviations of Cs-137 concentrations were noticed. To gain insight into cesium dynamics in shallow seafloor, long sediment cores were collected at shallow region near the FDNPP, and the vertical profiles of Cs-137 concentration and particle size distribution were determined. At the beach, Cs-137 concentration and particle size distribution were very homogenized from several tens of cm to more than 1 m deep, probably due to strong vertical mixing by wind waves and tides. Therefore, beach sediments have significant Cs-137 reserves in deeper layers at present. It was suggested that the Cs-137 supply from deep layers as well as the land area might suppress the decline of surface Cs-137 concentration in this area. At sampling points located at the bases of cliffs and depressions at the offshore zone, the vertical distributions of Cs-137 concentration were highly heterogeneous, showing the particle size dependency. Moreover, Cs-137 profiles obtained at the same point for several years were quite different. Therefore, it might cause the large fluctuation of Cs-137 concentration at surface sediment over time.
Sanada, Yukihisa; Misono, Toshiharu; Shiribiki, Takehiko*
Kaiyo Riko Gakkai-Shi, 27(2), p.37 - 44, 2023/12
This paper summarizes the general situation of marine monitoring conducted after the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, the experience of development and operation of USVs, and the possibility of applying unmanned vessels as a tool for nuclear disaster prevention in the future. 0.01 Bq/L or less for seawater and 10 Bq/L or less for seabed soil. Operational tests of three USVs have been continuously conducted for use in such environmental radiation monitoring. Development of these UAVs is underway with a view to utilizing them for seawater sampling, direct measurement of the seafloor soil surface layer, and seafloor soil sampling, depending on their performance. It is necessary to promote the development of USVs for future nuclear power plant accidents.
 I in the seabed sediment off Fukushima
I in the seabed sediment off FukushimaOtosaka, Shigeyoshi; Sato, Yuhi*; Suzuki, Takashi; Kuwabara, Jun; Nakanishi, Takahiro
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 192, p.208 - 218, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:47.7(Environmental Sciences)From August 2011 to October 2013, the concentration of iodine-129 ( I) in the seabed sediment collected from 26 stations located within 160 km from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant was estimated. The concentrations of
I) in the seabed sediment collected from 26 stations located within 160 km from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant was estimated. The concentrations of  I in seabed sediment off Fukushima in 2011 ranged between 0.02 and 0.45 mBq/kg. Although iodine is a biophilic element, the accident-derived radioiodine negligibly affects the benthic ecosystem. Until October 2013, a slightly increased activity of
I in seabed sediment off Fukushima in 2011 ranged between 0.02 and 0.45 mBq/kg. Although iodine is a biophilic element, the accident-derived radioiodine negligibly affects the benthic ecosystem. Until October 2013, a slightly increased activity of  I in the surface sediment in the shelf-edge region (bottom depth: 200-400 m) was observed. The increase of the
I in the surface sediment in the shelf-edge region (bottom depth: 200-400 m) was observed. The increase of the  I concentrations in the shelf-edge sediments was affected by the (1) transport of
I concentrations in the shelf-edge sediments was affected by the (1) transport of  I-bound particles from the land through rivers and (2) re-deposition of
I-bound particles from the land through rivers and (2) re-deposition of  I desorbed from the contaminated coastal sediment to the shelf-edge sediments, which were considered to be dominant processes.
I desorbed from the contaminated coastal sediment to the shelf-edge sediments, which were considered to be dominant processes.
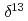 C and
C and 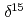 N values of sediment-trap particles in the Japan and Yamato Basins and comparison with the core-top values in the East/Japan Sea
N values of sediment-trap particles in the Japan and Yamato Basins and comparison with the core-top values in the East/Japan SeaKhim, B.-K.*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Park, K.-A.*; Noriki, Shinichiro*
Ocean Science Journal, 53(1), p.17 - 29, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:26.64(Marine & Freshwater Biology)Distribution of carbon and nitrogen stable isotope ratios (
 C,
C, 
 N) in sinking particles collected in four stations in the Japan Sea was summarized. The
N) in sinking particles collected in four stations in the Japan Sea was summarized. The 
 C and
C and 
 N values in the sinking particles showed a clear seasonal variation, which agreed well with the variation in the chlorophyll a concentration in the surface seawater and in the sinking flux of biogenic particles. In particular, during the highly productive season of phytoplankton, a remarkable isotopic fractionation of
N values in the sinking particles showed a clear seasonal variation, which agreed well with the variation in the chlorophyll a concentration in the surface seawater and in the sinking flux of biogenic particles. In particular, during the highly productive season of phytoplankton, a remarkable isotopic fractionation of 
 N was found in the sinking particles, and it was inferred that the fractionation indicates the degree of nitrogen uptake by diatoms in the surface layer. These results are helpful information for linking the phenomenon in the ocean surface and the isotopic information recorded in the seafloor.
N was found in the sinking particles, and it was inferred that the fractionation indicates the degree of nitrogen uptake by diatoms in the surface layer. These results are helpful information for linking the phenomenon in the ocean surface and the isotopic information recorded in the seafloor.
 Cs activity concentrations in sediment collected off the coast of Fukushima Prefecture in 2013-2015
Cs activity concentrations in sediment collected off the coast of Fukushima Prefecture in 2013-2015Fukuda, Miho*; Aono, Tatsuo*; Yamazaki, Shinnosuke*; Ishimaru, Takashi*; Kanda, Jota*; Nishikawa, Jun*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi
Geochemical Journal, 52(2), p.201 - 209, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.31(Geochemistry & Geophysics)To elucidate recent activity levels and the behavior of radiocesium in the coast off Fukushima Prefecture, lateral and vertical distributions of  Cs in sediment were observed in 2013-2015 at 12 monitoring stations. At stations around the water depth of 100 m, relatively higher
Cs in sediment were observed in 2013-2015 at 12 monitoring stations. At stations around the water depth of 100 m, relatively higher  Cs activities were observed from surface sedimentary layer (0-3 cm). In these stations, sediments had high content of silt to clay particles and organic matter. The high
Cs activities were observed from surface sedimentary layer (0-3 cm). In these stations, sediments had high content of silt to clay particles and organic matter. The high  Cs activities in the surface sediments were attributed to accumulation of highly mobile sediment particles. In October 2014, at some coastal stations, sharp peaks of
Cs activities in the surface sediments were attributed to accumulation of highly mobile sediment particles. In October 2014, at some coastal stations, sharp peaks of  Cs activities were observed in the subsurface (5-16 cm) sediments, whereas such broad peaks were not found in October 2015. These results suggest that the
Cs activities were observed in the subsurface (5-16 cm) sediments, whereas such broad peaks were not found in October 2015. These results suggest that the  Cs activities in sediment had largely changed by lateral transport and re-sedimentation on the surface, as well as sediment mixing in the middle-layers.
Cs activities in sediment had largely changed by lateral transport and re-sedimentation on the surface, as well as sediment mixing in the middle-layers.
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Kobayashi, Takuya; Machida, Masahiko
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 59(11), p.659 - 663, 2017/11
, 59(11), p.659 - 663, 2017/11
It is estimated that about 70% of radiocesium released to the environment by the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident was carried to the ocean. In addition to monitoring surveys by the government, oceanographic research by many institutions has revealed the distribution and behavior of the accident-derived radiocesium in the ocean. Numerical simulations are efficiently used in such oceanographic investigations, and further improvements are being made based on findings newly obtained after the accident. In this paper, we review the abundance and behavior of radiocesium in the coastal area of Fukushima, deepen the scientific understanding of the current situation of environmental restoration, and explain the issues to be addressed in the future.
 Cs concentration in surface sediments off Fukushima
Cs concentration in surface sediments off FukushimaOtosaka, Shigeyoshi
Journal of Oceanography, 73(5), p.559 - 570, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:77.33(Oceanography)Based on monitoring data from 71 stations off the coast of Fukushima, Miyagi and Ibaraki Prefectures, changing tendencies of  Cs concentration in surface (0-10 cm) sediment are analyzed, and primary processes affecting the temporal changes are determined. In the coastal region (water depth
Cs concentration in surface (0-10 cm) sediment are analyzed, and primary processes affecting the temporal changes are determined. In the coastal region (water depth  100m), between 2011 and 2015, concentrations of
100m), between 2011 and 2015, concentrations of  Cs in the surface sediment decreased at the rate of 27% per year in average. Such a remarkable temporal change in the
Cs in the surface sediment decreased at the rate of 27% per year in average. Such a remarkable temporal change in the  Cs concentration of sedimentary radiocesium was not observed in the offshore regions. By applying observed data of vertical distribution of sedimentary
Cs concentration of sedimentary radiocesium was not observed in the offshore regions. By applying observed data of vertical distribution of sedimentary  Cs into a pulse input sediment mixing model, it was estimated that more than a half of the decreasing effect was explained by vertical mixing of
Cs into a pulse input sediment mixing model, it was estimated that more than a half of the decreasing effect was explained by vertical mixing of  Cs-bound surface sediment with less-contaminated sediment in the deeper layers.
Cs-bound surface sediment with less-contaminated sediment in the deeper layers.
Nagao, Seiya*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Kaeriyama, Hideki*
Journal of Oceanography, 73(5), P. 527, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:46.07(Oceanography)More than five years have passed since the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, and many investigations have been carried out in the marine environment. Regarding the radiocesium concentration in seabed sediment, from May 2011, monitoring survey is continuing mainly in the coastal areas of Miyagi, Fukushima, Ibaraki and Chiba prefectures. However, due to its heterogeneity, the difficulty of observation, etc., the assessment of the influence of the accident-derived radionuclides on seabed sediments and the benthic ecosystem is delayed compared to other environmental investigations. As the Guest Editors, the authors set up a special section in "Journal of Oceanography", including four papers arguing about factors affecting the temporal change of the radiocesium concentrations in estuarine, coastal and offshore sediments. This preface shows the planning intention of the special issue, and also outlines the contents.
Honda, Makio*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 58(4), p.225 - 228, 2016/04
, 58(4), p.225 - 228, 2016/04
Transport processes of particulate radiocesium obtained from a three year time-series sediment trap experiments at a site 115 km southeast of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant off Fukushima are expounded. Results show a high fraction of lithogenic material in sinking particles, suggesting a lateral source of sediments. In particular, we found that accident-derived radiocesium associate with slope and shelf sediments were resuspended and transported laterally to the offshore regions in typhoon seasons in 2013. Continuous observation of such transport processes of particulate radiocesium near the seabed would be significant for better understanding of the fate of accident-derived radiocesium.
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Suzuki, Takashi; Sato, Yuhi; Narita, Hisashi*
Environmental Science & Technology, 48(21), p.12595 - 12602, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:58.4(Engineering, Environmental)From August 2011 to July 2013, a sediment trap was deployed at 100 km east of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant and sinking particles were collected. Sinking flux of  Cs decreased over time with seasonal fluctuation. The
Cs decreased over time with seasonal fluctuation. The  Cs fluxes were mainly affected by two principal modes. One was a rapid sinking of radiocesium-bound particles (moderate mode). This mode was dominant especially in the early post-accident stage, and was presumed to establish the distribution of radiocesium in the offshore seabed. Another was the secondary transport of particles attributed to turbulence near the seabed and was observed in winter (turbulence mode). Although the latter process would not drastically change the distribution of sedimentary radiocesium, attention should be paid as this key process redistributing the accident-derived radiocesium may cumulatively affect the long-term distribution.
Cs fluxes were mainly affected by two principal modes. One was a rapid sinking of radiocesium-bound particles (moderate mode). This mode was dominant especially in the early post-accident stage, and was presumed to establish the distribution of radiocesium in the offshore seabed. Another was the secondary transport of particles attributed to turbulence near the seabed and was observed in winter (turbulence mode). Although the latter process would not drastically change the distribution of sedimentary radiocesium, attention should be paid as this key process redistributing the accident-derived radiocesium may cumulatively affect the long-term distribution.
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Amano, Hikaru; Ito, Toshimichi; Kawamura, Hideyuki; Kobayashi, Takuya; Suzuki, Takashi; Togawa, Orihiko; Chaykovskaya, E. L.*; Lishavskaya, T. S.*; Novichkov, V. P.*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 91(3), p.128 - 145, 2006/00
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:42.09(Environmental Sciences)Distributions of radionuclides ( Sr,
Sr,  Cs and
Cs and  Pu) in seabed sediment in the Japan Sea were observed during 1998-2002. Observed inventories of anthropogenic radionuclides in sediment ranged 0.1-86 Bq m
Pu) in seabed sediment in the Japan Sea were observed during 1998-2002. Observed inventories of anthropogenic radionuclides in sediment ranged 0.1-86 Bq m for
for  Sr, 23-379 Bq m
Sr, 23-379 Bq m for
for  Cs and 0.1-86 Bq m
Cs and 0.1-86 Bq m for
for  Pu. In the deep part (
Pu. In the deep part ( 2 km depth) of the western Japan Basin,
2 km depth) of the western Japan Basin,  Pu/
Pu/ Cs inventory ratios were larger than those in the central Yamato Basin although inventories of radionuclides were not different between basins. The higher
Cs inventory ratios were larger than those in the central Yamato Basin although inventories of radionuclides were not different between basins. The higher  Pu/
Pu/ Cs ratios in the western Japan Basin were derived by the production of Pu-enriched particle in the surface layer and effective sinking of particulate materials in this region. In the marginal Yamato Basin and the Ulleung Basin, both inventories and
Cs ratios in the western Japan Basin were derived by the production of Pu-enriched particle in the surface layer and effective sinking of particulate materials in this region. In the marginal Yamato Basin and the Ulleung Basin, both inventories and  Pu/
Pu/ Cs ratios in sediment were larger than those in the central Yamato Basin. In the eastern/southern Japan Sea, it was suggested that the supply of particulate radionuclides by the TWC enhanced accumulation of radionuclides in this region.
Cs ratios in sediment were larger than those in the central Yamato Basin. In the eastern/southern Japan Sea, it was suggested that the supply of particulate radionuclides by the TWC enhanced accumulation of radionuclides in this region.
 Pb in the northwestern Japan Sea
Pb in the northwestern Japan SeaOtosaka, Shigeyoshi; Baba, Masami*; Togawa, Orihiko; Karasev, E. V.*
Pacific Oceanography, 1(2), p.149 - 157, 2003/12
A sediment trap experiment and sediment coring were carried out in the northwestern Japan Sea (Sta MS), and lead-210 ( Pb) and major components in settling particles were measured. By drawing up a balance of
Pb) and major components in settling particles were measured. By drawing up a balance of  Pb in the water column, it was estimated that the cycle of
Pb in the water column, it was estimated that the cycle of  Pb in the Sta MS was controlled by 3 processes, (1) removal and vertical transport of
Pb in the Sta MS was controlled by 3 processes, (1) removal and vertical transport of  Pb from the surface layer by settling particles, (2) decomposition of particles in the deep layer, and (3) export by the deep current. Flux of
Pb from the surface layer by settling particles, (2) decomposition of particles in the deep layer, and (3) export by the deep current. Flux of  Pb at 3 km depth was large in winter and spring. The large
Pb at 3 km depth was large in winter and spring. The large  Pb flux in this season would be caused by the horizontal import of
Pb flux in this season would be caused by the horizontal import of  Pb -rich seawater from the coastal region to the bottom layer of Sta MS. It was suggested that seasonal variation of particulate
Pb -rich seawater from the coastal region to the bottom layer of Sta MS. It was suggested that seasonal variation of particulate  Pb flux at the deep layer in the northwestern Japan Basin indicated the renewal of the deep water in this area.
Pb flux at the deep layer in the northwestern Japan Basin indicated the renewal of the deep water in this area.
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Aramaki, Takafumi*; Suzuki, Takashi; Kobayashi, Takuya; Ito, Toshimichi; Togawa, Orihiko; Chaykovskaya, E. L.*; Dunaev, A. L.*; Karasev, E. V.*; Novichkov, V. P.*; et al.
Proceedings of International Symposium on Radioecology and Environmental Dosimetry, p.390 - 395, 2003/10
Seabed sediments were collected at 22 stations in the Japan Sea, and anthropogenic radionuclides were measured in order to understand distributions and accumulation processes of these materials. Averaged concentrations of  Cs in sediment in the Japan Basin and the Yamato Basin were 1.0 Bq/kg and 1.0 Bq/kg, respectively. Although there was no significant difference in mean
Cs in sediment in the Japan Basin and the Yamato Basin were 1.0 Bq/kg and 1.0 Bq/kg, respectively. Although there was no significant difference in mean  Cs concentration between the Japan Basin and the Yamato Basin, distributions of radionuclides in these 2 basins showed different features. In the Japan Basin, the spatial variation of concentration of radionuclides was smaller than that at the Yamato Basin. At most stations in the Yamato Basin, significant concentrations of radionuclides were not detected, but remarkable large activities were observed at several stations in the Yamato Basin. For all radionuclides, the highest concentration was observed in the southeastern margin of the Yamato Basin. These results would suggest that there were different accumulation processes of radionuclides between the Japan Basin and the Yamato Basin.
Cs concentration between the Japan Basin and the Yamato Basin, distributions of radionuclides in these 2 basins showed different features. In the Japan Basin, the spatial variation of concentration of radionuclides was smaller than that at the Yamato Basin. At most stations in the Yamato Basin, significant concentrations of radionuclides were not detected, but remarkable large activities were observed at several stations in the Yamato Basin. For all radionuclides, the highest concentration was observed in the southeastern margin of the Yamato Basin. These results would suggest that there were different accumulation processes of radionuclides between the Japan Basin and the Yamato Basin.
Sumiya, Shuichi; Hayashi, Naomi; ; Narita, Osamu
PNC TN8430 91-001, 45 Pages, 1990/12
A radioanalytical method for low level samarium-151(Sm-151) and promethium-147(Pm-147) in environmental samples has been studied for the environmental assessment around nuclear facilities. In this study, we use the separation method with high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to determine Sm-151 and Pm-147 in environmental samples such as sea sediments and marine organisms. Samarium-151 and Pm-147 in environmental samples are coprecipitated with other lanthanoids after adding neodymium(Nd). These nuclides are purified by anion exchange methods in methanol-mineral acid media. After the purification, Sm-151 and Pm-147 are separated with HPLC in lactic acid-sodium hydroxide media, and determined with liquid scintillation counting, respectively. The Nd is determined by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES) to correct chemical recoveries of these nuclides. The detection limits for Sm-151 and Pm-147 in this method are about 0.01Bq/sample.
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Sato, Yuhi; Suzuki, Takashi; Narita, Hisashi*
no journal, ,
A sediment trap experiment was conducted between August 2011 and July 2013 and sinking particles were collected at 100 km east of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. Sinking flux of  Cs was the highest in September 2011 (98 mBq/m
Cs was the highest in September 2011 (98 mBq/m /day), and decreased over time with seasonal fluctuation. The sinking fluxes of particulate radiocesium were controlled by two modes. One was a rapid sinking of radiocesium-bound particles (summer mode). This mode was dominant especially in the early post-accident stage, and was presumed to establish the distribution of radiocesium in the offshore seabed. Another was the secondary transport of particles attributed to turbulence near the seabed and was observed in winter (winter mode). Although the latter process would not change the distribution of sedimentary radiocesium drastically, attention should be paid as a key process redistributing the accident-derived radiocesium over a long duration.
/day), and decreased over time with seasonal fluctuation. The sinking fluxes of particulate radiocesium were controlled by two modes. One was a rapid sinking of radiocesium-bound particles (summer mode). This mode was dominant especially in the early post-accident stage, and was presumed to establish the distribution of radiocesium in the offshore seabed. Another was the secondary transport of particles attributed to turbulence near the seabed and was observed in winter (winter mode). Although the latter process would not change the distribution of sedimentary radiocesium drastically, attention should be paid as a key process redistributing the accident-derived radiocesium over a long duration.